Block vs Object vs File storage
| Feature | Object Storage | Block Storage | Network Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Unit | Object (data + metadata) | Block (raw data chunks) | File (organized in paths) |
| Access Method | Restful APIs | FC/iSCSI | NFS/SMB |
| Use Case | Archival, media storage | Databases, VMs | Shared file access |
| Performance | High scalability | High IOPS, low latency | Moderate performance |
what are root causes of deadlock?
4 conditions happen at the same time:
- Mutual Exclusion
- Hold and Wait
- No Preemption (no process is able to force another process release resource)
- Circular Wait
What is machine code
Code executed by CPU
machine code vs byte code
| Machine code | Byte code |
|---|---|
| instructions run by CPU | code run by virtual machine (JVM, V8) |
What kind of file does Rust compile to?
Machine code
What tools are used to read instruction from binary file?
obj_dump & xxd CLI
How many types of instruction?
- Data Movement: move data between registers, memory, and I/O devices.
- Arithmetic: perform mathematical operations on data.
- Logical: perform logical operations on binary data.
- Control Flow: alter the sequence of execution in a program.
- Comparison: compare two operands and set condition flags based on the result.
- Shift and Rotate: perform bit-shifting or bit-rotation operations on data.
- Input/Output: handle communication between the processor and external devices or memory.
- Nop (No Operation) NOP: A no-operation instruction that does nothing. It is often used for timing, debugging, or alignment purposes.
- Exception and Interrupt: manage interrupt handling and exceptions.
- System Control: interact with the system or control the processor’s behavior.
- Floating Point: handle floating-point operations, which are important for calculations that involve real numbers.
Stack vs Heap vs Static memory
| stack | heap | static memory |
|---|---|---|
| scoped | ownership | program duration |
| LIFO | jumping from 1 pointer to another | data/BSS segment |
what are the differences between &String and &str ?
| Feature | String | &str | &String |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned, heap-allocated | Borrowed, immutable | Borrowed reference |
| Mutability | Mutable | Immutable | Immutable |
| Memory | Heap | Stack or Heap | Heap |
| Conversion | Can be borrowed as &str | Can be converted to String | Automatically coerces to &str |
| Typical Use | Owned, growable string | Immutable view of data | Immutable borrowed view |
How does Scheduler create a Pod?
- Scheduler does not create a Pod
- Scheduler scores node (affinity, taint, toleration, …) -> notify API server -> ETCD
- Kubelet get info from API server-> create container
How a new pod is created in Kubernetes cluster?
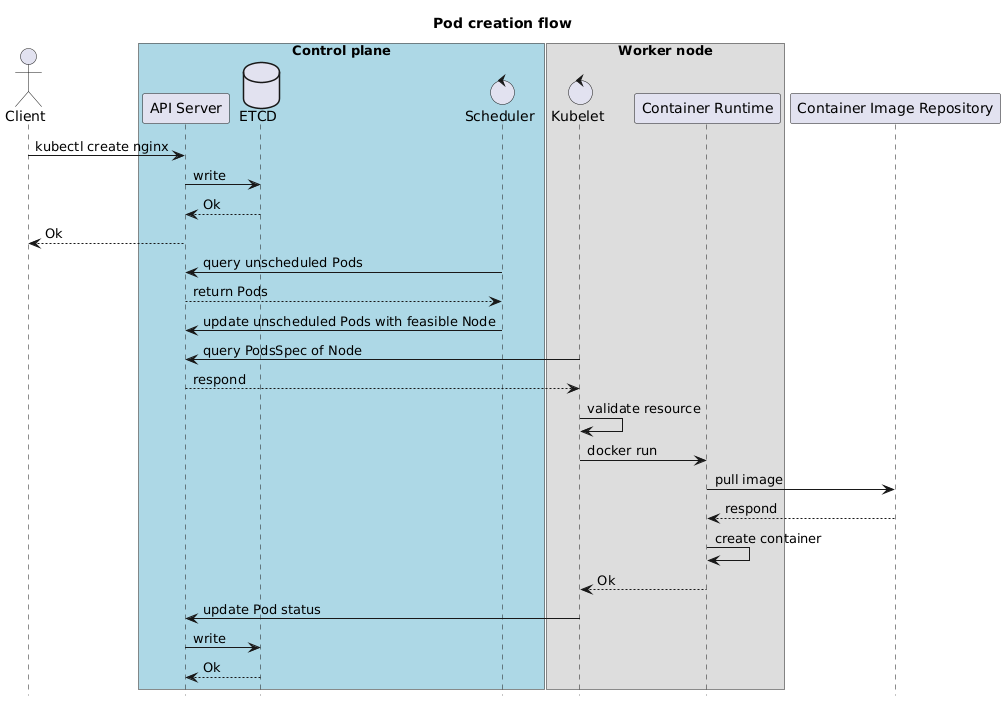
how it score nodes???
manage platform service (operation) là làm những gì???
- installation
- incident management
- downtime management
- update & patching
- observability
- config management
- performance optimization
- optimize system components
- reduce bottle neck
- …
- backup & recovery
- Hardening
- Cost optimization
Does downtime happen when an incident occur?
scheduled downtime
term dung de tranh downtime incident? plan han che code + ops ngu
What is Hardening? vs Computer Security???
- Secure Coding ??
- scan code for sensitive content
- scan dependencies
- enforce Authn and Authz
- data encryption
what can Kong do?
API Gateway Ingress Controller
What API Gateway can do? giai quyet van de gi???
- centralizes API requests
- applies policies
- manages routing
What the differences between ingress, egress and api gateway?
| Feature | Ingress | Egress | API Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing incoming traffic to services. | Managing outgoing traffic to external systems. | Managing API traffic (both ingress & egress). |
| Scope | Network-level HTTP/HTTPS traffic. | Network-level outbound traffic. | Application-level API requests and responses. |
| Key Functionality | Routing, SSL termination, load balancing. | Traffic control, security, monitoring. | Authentication, rate limiting, monitoring, routing. |
| Use Case | Exposing services to external clients. | Restricting or monitoring outgoing traffic. | Centralized API management for microservices. |
| Example Tools | Nginx, Traefik, Kubernetes Ingress. | Egress Gateways (Istio, Calico). | Kong, Istio, Amazon API Gateway, Apigee. |
tại sao chạy e2e test using docker compose ?
-> embbed postgres (jonkey)
worker gọi master khi nào và ngược lại?
kubelet
What are use cases for each types of AWS Load Balancer?
| Feature | Application LB (ALB) | Network LB (NLB) | Gateway LB (GWLB) | Classic LB (CLB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | 7 (Application) | 4 (Transport) | 3 (Network) | 4 & 7 |
| Protocols | HTTP, HTTPS, WebSocket | TCP, UDP, TLS | IP | HTTP, HTTPS, TCP |
| Advanced Routing | Path, Host-based | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| Targets | EC2, Lambda, IPs, Containers | EC2, IPs | Virtual Appliances | EC2 only |
| Latency | Moderate | Ultra-low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Best for | Web applications, APIs | Real-time applications | Security tools | Legacy workloads |
not ALB -> CLB ? when we need other protocol in layer 7 (DNS, SMTP, FTP,…) except HTTP & HTTPS not NLB -> CLB ? when you need features like Sticky Sessions, SSL Termination apply tracing into Morpheuslabs, Zipkin
worker gọi master khi nào và ngược lại?
Why API Server not sending request to Kubelet, but Kubelet have to make a request to API Server??? Not yet
- Scalability
- Each connection to API Server will be manage by Kubelet
- Reduce the heavy workload for API Server in pull-based model
- Reliability
- In push model, if the API Server fail every
pendingrequest will be lost - In pull model, Kubelet will operate the retry mechanism base on the last known state
- API Server + ETCD act as a source of truth, they don’t have to manage the Kubelet state
How to measure performance of a (MySQL) server???
- Throughput: Measures how many queries MySQL can process in a second. Example: 10,000 queries executed in 10 seconds = 1,000 QPS. Formula:
Throughput=Total Queries Executed/Execution Time - Latency (Execution Time): The time it takes to execute a single query.
- Connections (Concurrency): Maximum concurrent connections supported without degradation in performance.
- I/O Performance: Measures the speed of read/write operations
before coredns is there any mechanism to resolve DNS in k8s cluster???
Kube-DNS (https://github.com/kubernetes/dns)
tool draw -> code -> diagram, có gọi là diagram as code ko? dựa vào đâu gọi nó là diagram as code?
CODE as source of truth
What is digital signatures
How pub/sec keys of CA are use in PKI?
pub -> decrypt | prv -> encrypt
normal case, encrypt = pub key because multi clients -> server decrypt (harder) => prv (need to protect) uses for decrypt
digital signature, encrypt = prv (harder) only server can encrypt, pub key used to decrypt
diff CA digital signature (DS) vs server DS
what does server’s certificate used for?
- Authentication
- Encryption
what is a protocol?
A set of rules for:
- formatting
- processing data
Example: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Data process:
- Connection setup: 3-way handshake
- Data transmission: send & acknowledge data packet
Format:
- TCP Header Example:
[Source Port: 16 bits][Destination Port: 16 bits] [Sequence Number: 32 bits][Acknowledgment Number: 32 bits] [Data Offset][Flags][Window Size][Checksum][Urgent Pointer]- Data Section: Contains the payload being transmitted.
why protocols is needed?
These rules are used to create a common language for computers which use different software but still want to communicate to each other
what is TLS?
- security protocol
- designed to facilitate privacy and data security
what is mTLS?
an extension of TLS, not only Server send certificate to Client but the Client also need to send its certificate to Server
in K8s use TLS or mTLS? where?
- mTLS is used to communicate internally in the cluster
- TLS is used for external client (e.g. a client send a request to a service in K8s cluster)
can we CA in k8s cluster for web?
- No, because the root CA can not be downloaded by client
EKS authn request from kubectl?
IAM role + access entry -> cluster user
Service to pod
Over the different iterations of Kubernetes, the method in favor of enabling this has changed, but the two main methods are via
- the use of iptables (mostly) -> a pseudo L4 LB
- the newer IP Virtual Server (IPVS)
- eBPF-based dataplane (from cloud)
Network plugin-ins types
- kubenet (simple, dont consume IP -> routing mechanism???)
- plug-ins follows CNI specification
What is the term to describe the seperation of seperate control plane & data plane?
Decoupling
What does Control/Data Plane need?
Control plane: Consistent
Data plane: Reliable
why ETCD is chosen?
(C)onsistency & (P)artition Tolerance (NoSQL??) in CAP
Does ETCD still achieve high availability, after choosing CP?
Yes, but it requires more effort to make it achieve HA
- frequently backup
- manage Quorum properly (odd-number)
Why should ETCD number of nodes be kept as odd-number?
- optimally maximize High Availability, for example: both 3 nodes and 4 nodes cluster can tolerate 1 failure node
- increase chance of partition
which object will do load balance Ingress or Service?
Answer: both
Ingress:
- Layer 7
- When the Service that Ingress routes to is a headless Service
Service:
- Layer 3
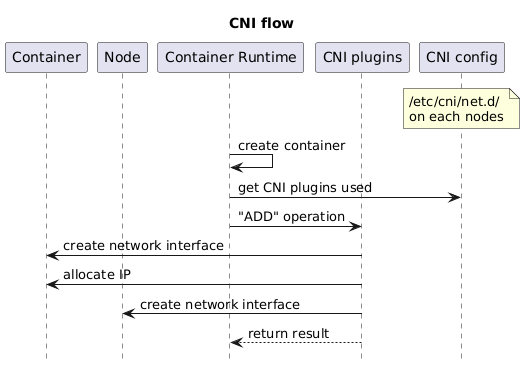
flow of IP allocation by CNI
Fault Tolerance vs HA
0 downtime vs 99,999%
Scaling vs Elastic
elastic = scale in/out AND up/down while scaling up/out